3. Tidal
This example demonstrates use of MODFLOW 6 observations and time series and the capability to use multiple stress packages of the same type in a single groundwater flow model. This is a synthetic example problem that has not been documented elsewhere.
3.1. Example Description
The problem consists of two aquifers, which are separated from each other by a confining layer. The upper aquifer is unconfined and the lower aquifer is confined. The confining layer is 15 \(m\) thick and is explicitly simulated as model layer 2. The grid consists of 15 rows and 10 columns. Each cell is 500 \(m\) on a side. A single steady-stress period of 1 day is followed by three 10-day transient stress periods, each with 120 time steps. Model parameters are listed in Table 3.1.
Parameter |
Value |
|---|---|
Number of periods |
4 |
Number of layers |
3 |
Number of columns |
10 |
Number of rows |
15 |
Column width (\(m\)) |
500.0 |
Row width (\(m\)) |
500.0 |
Top of the model (\(m\)) |
50.0 |
Layer bottom elevations (\(m\)) |
5.0, –10.0, –100.0 |
Starting head (\(m\)) |
50.0 |
Cell conversion type |
1, 0, 0 |
Horizontal hydraulic conductivity (\(m/d\)) |
5.0, 0.1, 4.0 |
Vertical hydraulic conductivity (\(m/d\)) |
0.5, 5.0e-3, 0.1 |
Specific storage (\(/m\)) |
1.0e-6 |
Specific yield (unitless) |
0.2 |
An initial head of 50 \(m\) was specified in all model layers. Any initial head exceeding the bottom of model layer 1 (5 \(m\)) could be specified since the model is steady-state.
The model demonstrates use of the GHB, WEL, RIV RCH, and EVT stress packages. Locations for these boundaries are shown in Figure 3.1. The GHB is used to apply a tidally varying boundary condition to the right side of the model in layers 2 and 3. The GHB Package uses the time series capability to represent tidally varying stage for these stress boundaries. Stage values are linearly interpolated to each time step from a time series of tidal fluctuations. The WEL Package also uses time series to change pumping rates by well according to a time series of pumping records. The pumping rates are interpolated using the stepwise option, which indicates that rates are held constant at the specified value until a new value is specified. This is an alternative to the linear interpolation method. The WEL Package contains pumping rates specified with time series and pumping rates specified with a constant value for the stress period. A simple RIV Package is also used with time series to change the river stage by time step.
The RCH and EVT Packages are used to assign and calculate recharge and evapotranspiration, respectively. Three separate RCH Packages are used in this example to assign a different recharge rate to each of the three zones shown in Figure 3.1D.
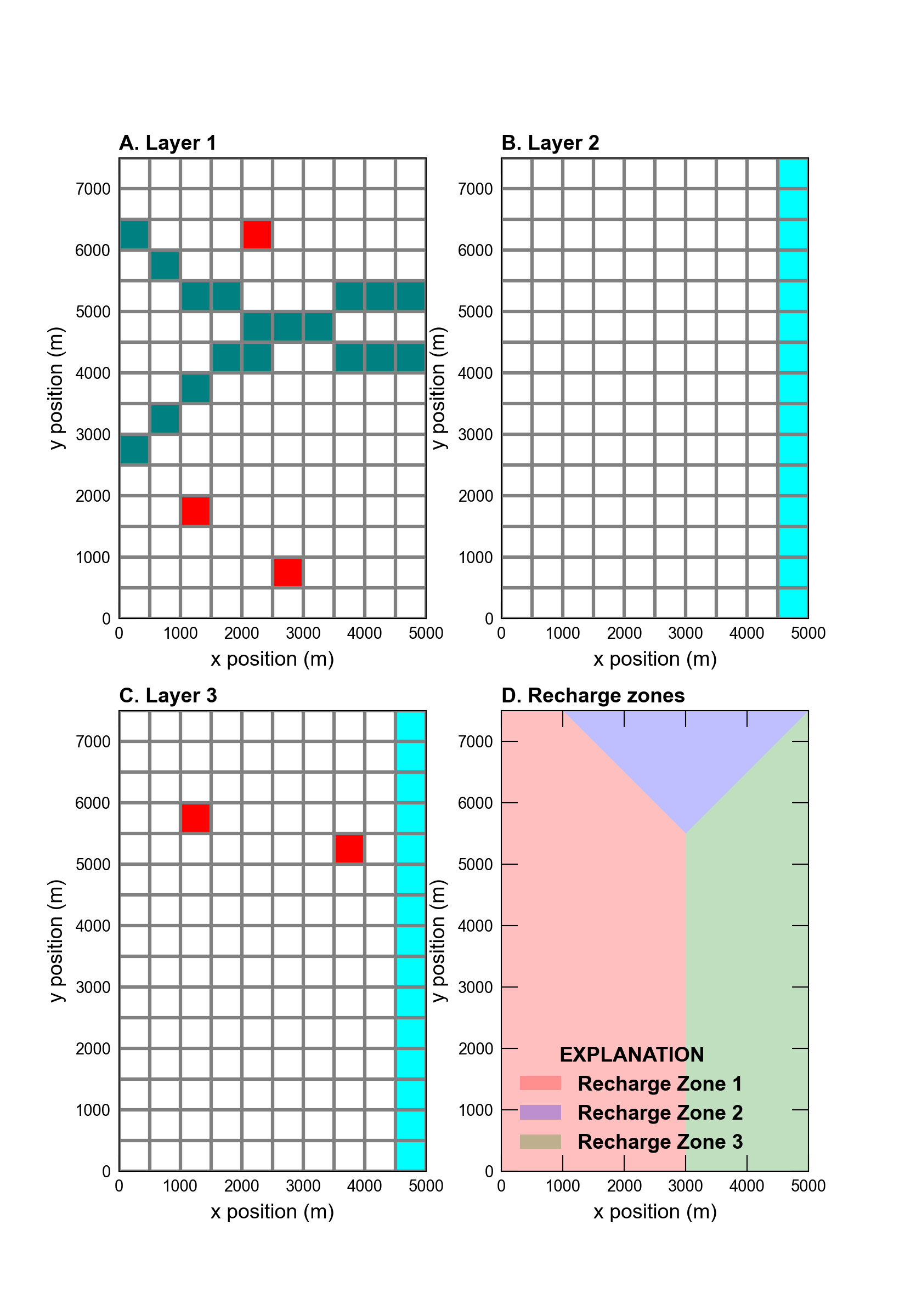
Figure 3.1 Model grid and boundary conditions used for the Tidal example problem: (A) river and well boundaries in layer 1; (B) general-head boundaries in layer 2; (C) general-head and well boundaries in layer 3; and (D) zones used to assign recharge to layer 1.
3.2. Example Results
The observation capability in MODFLOW 6 was used to extract time series of simulated heads and flows. Time series of model results are shown in Figure 3.2, Figure 3.3, and Figure 3.4.
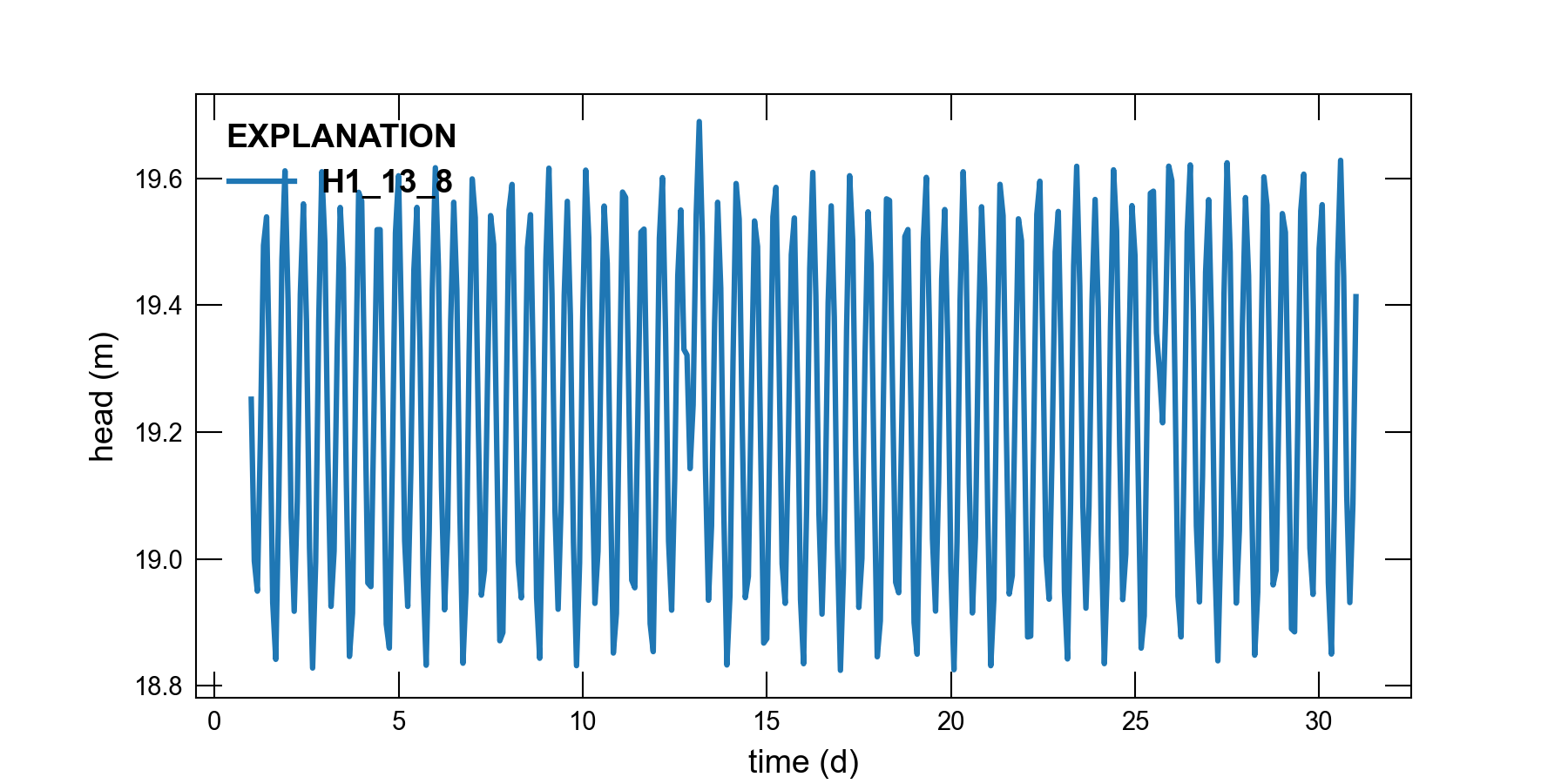
Figure 3.2 Simulated groundwater head in model cell (1, 13, 8).
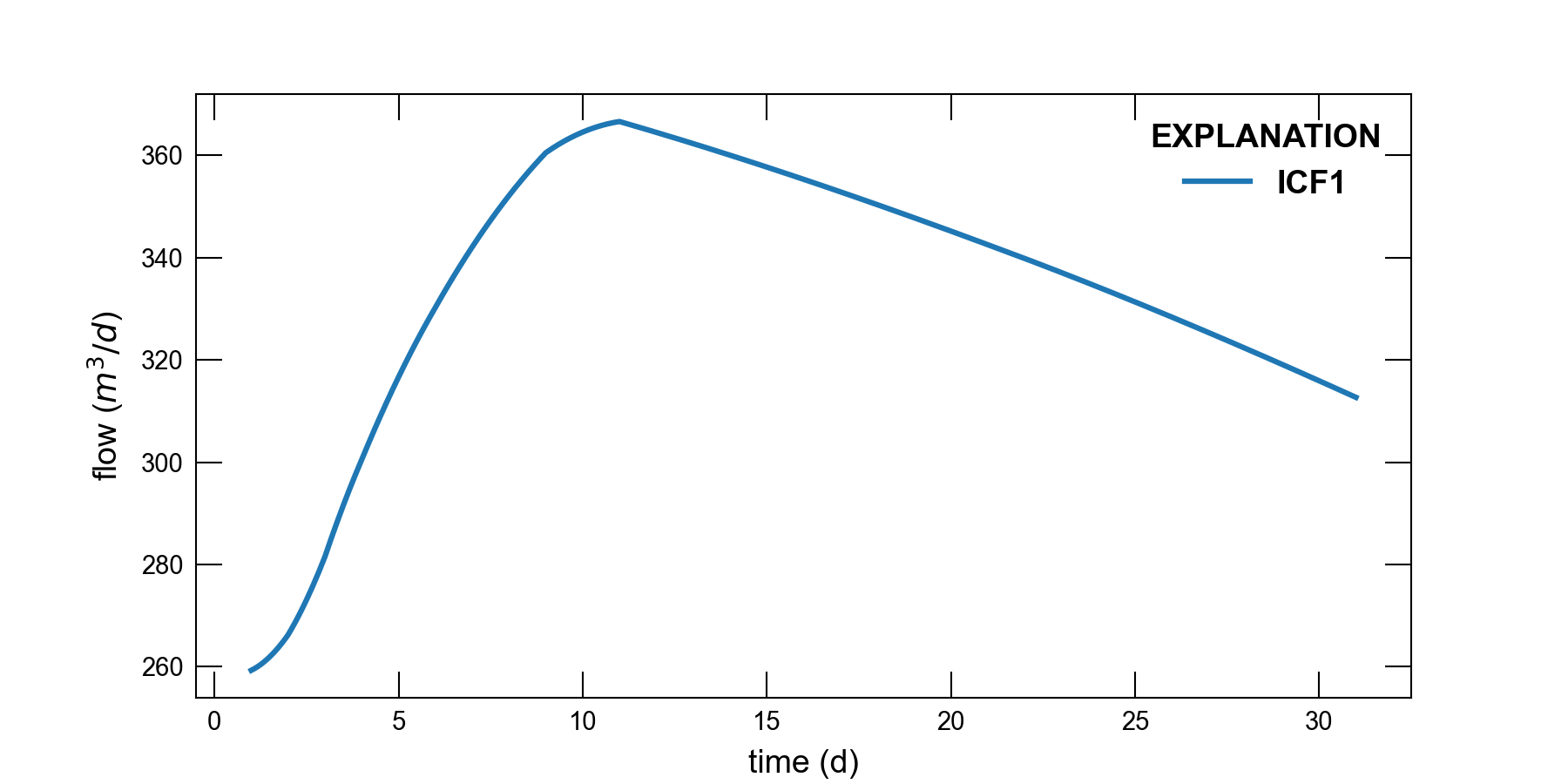
Figure 3.3 Simulated groundwater flow for model cell (1, 5, 6) and its connection with model cell (1, 6, 6). Positive values indicate flow into model cell (1, 5, 6).
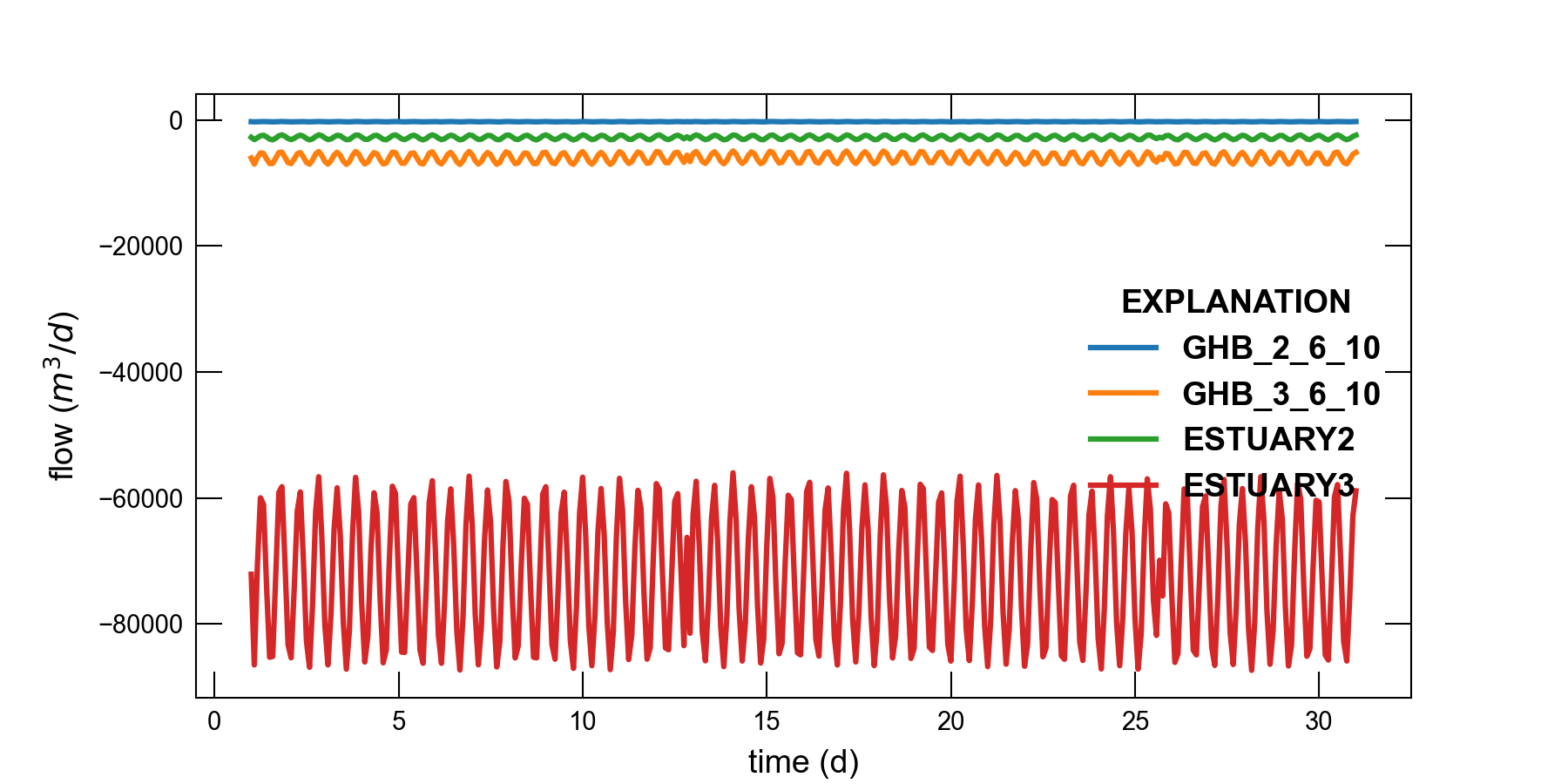
Figure 3.4 Simulated flow between general-head boundary cells and the groundwater flow model. ESTUARY2 is the combined flow for all general-head cells in layer 2. ESTUARY3 is the combined flow for all general-head cells in layer 3. A positive value represents from from the general-head boundary into the groundwater model.
3.3. Jupyter Notebook
The Jupyter notebook used to create the MODFLOW 6 input files for this example and post-process the results is: